Urethral Discharge In Men
exp date isn't null, but text field is
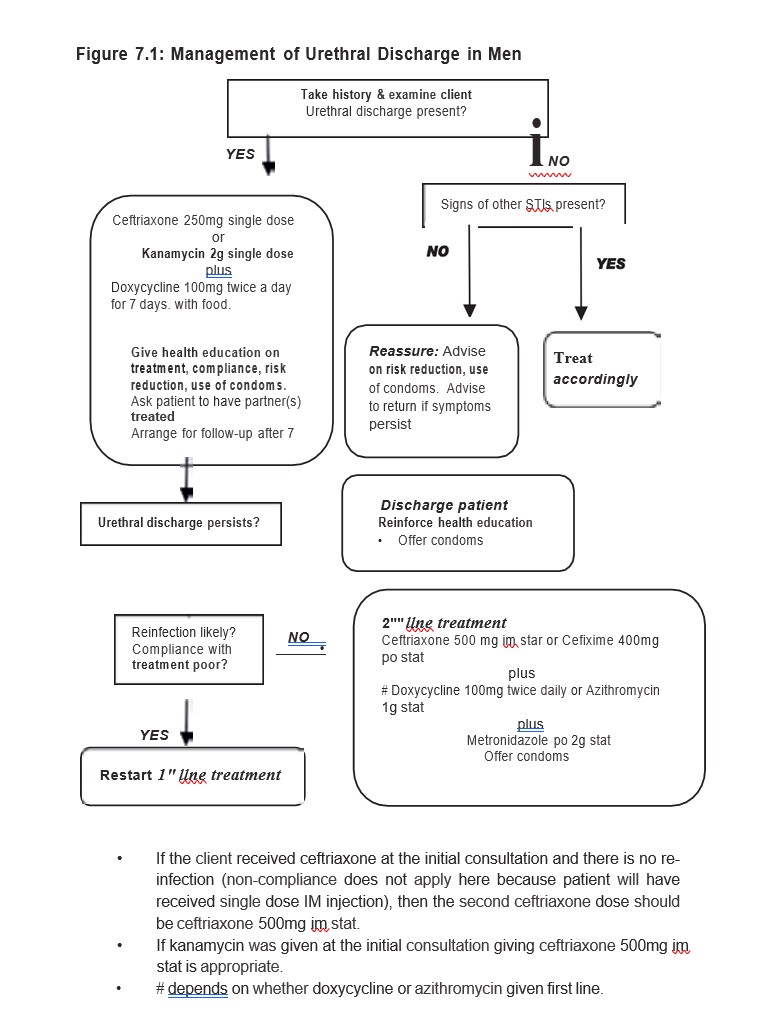
The commonest causes are Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Chlamydia trachomatis, and the two often co-exist. Trichomonas vaginalis also causes a urethral discharge in men. All males with urethral discharge and all women with cervicitis should be treated for both gonorrhoea and chlamydia in view of the fact that the two coexist and present with similar signs and symptoms. Any sex partners in the preceding three months should be treated presumptively for the same infections as in the index patient, and any other conditions found on examination Recent studies (2015) from Zimbabwe showed that a small proportion of men with urethral discharge have Mycoplasma genitalium.
First Line:
|
Medicine |
Adult dose |
Frequency / Duration |
|
|
ceftriaxone im |
250mg |
one dose only |
|
|
or |
kanamycin im |
2g (1g in each buttock) |
one dose only |
|
and |
doxycycline po |
100mg |
twice a day for 7 days |
|
or |
azithromycin po |
1g |
one dose only |
If the patient still has a urethral discharge, or evidence of urethritis 7 days after start of treatment, suspect re-infection, poor treatment compliance or antimicrobial resistance in Neisseria gonorrhoeae. If re-infection is suspected re-start first line treatment.
Otherwise treat the patient with second line therapy or refer for investigations and laboratory guided treatment.
Second Line:
|
Medicine |
Adult dose |
Frequency / Duration |
|
|
ceftriaxone im |
500mg |
one dose only |
|
|
or |
cefixime po |
400mg |
one dose only |
|
and |
metronidazole po |
2g |
one dose only |
|
and |
doxycycline po (Dependent on 1st line Rx* if 1st line Azithromycin) |
100mg |
twice a day for 7 days |
|
or |
azithromycin po (if 1st line doxycycline) |
1g stat than 500mg od for 2 days |
3 days |
*New evidence suggests this approach which is updated from Zimbabwe STI guidelines
- If these medicines are not available locally, refer to the next level.