Genital Ulcer Disease (GUD) Syndrome
exp date isn't null, but text field is
ICD10 CODES: N76.5-6, N48.5
Genital ulcer syndrome is one of the commonest syndromes that affect men and women. Single or multiple ulcers can be present.
Causes
Multiple organisms can cause genital sores, commonly:
- Treponema pallidum bacteria: syphilis
- Herpes simplex virus: genital herpes
- Haemophilus ducreyi: Chancroid
- Donovania granulomatis: Granuloma inguinale
- Chlamydia strains: lymphogranuloma venerium (LGV)
Clinical features
Mixed infections are common
- Primary syphilis: the ulcer is at first painless and may be between or on the labia or on the penis
- Secondary syphilis: multiple, painless ulcers on the penis or vulva
- Genital Herpes: small, multiple, usually painful blisters, vesicles, or ulcers. Often recurrent
- Granuloma inguinale: an irregular ulcer which increases in size and may cover a large area
- Chancroid: multiple, large, irregular ulcers with enlarged painful suppurating lymph nodes
Differential diagnosis
- Cancer of the penis in elderly men
- Cancer of the vulva in women >50 years
Investigations
- Swab: for microscopy
- Blood: for VDRL/TPR
Management
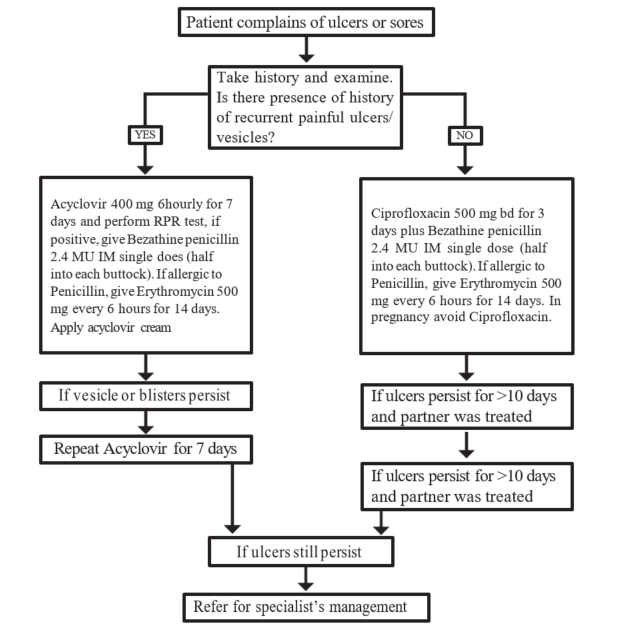
Treatment
| TREATMENT | LOC |
|
Multiple painful blisters or vesicles: likely herpes
|
HC4 HC3 |
|
All other cases
If ulcer persists >10 days and partner was treated
If ulcer still persists Refer for specialist management |
|
Note
- Negative RPR does not exclude early syphilis
- Genital ulcers may appear with enlarged and fluctuating inguinal lymph nodes (buboes). Do not incise buboes
