Abnormal Vaginal Discharge Syndrome
exp date isn't null, but text field is
ICD10 CODE: N76
Often the first evidence of genital infection, although absence of abnormal vaginal discharge does not mean absence of infection. Normal discharge is small in quantity and white to colourless. Not all vaginal infections are sexually transmitted diseases.
Causes
Can be a variety and often mixture of organisms
- Vaginitis: by Candida albicanis, Trichomonas vaginalis or bacterial vaginosis (by Gardnerella vaginalis, Mycoplasma hominis)
- Cervicitis: commonly due to gonorrhoea and chlamydia: usually asymptomatic and rarely a cause of abnormal vaginal discharge
Clinical features
- Increased quantity of discharge, abnormal colour and odour
- Lower abdominal pain, itching and pain at sexual intercourse may be present
- In Candida albicans vaginitis: very itchy thick or lumpy white discharge, red inflamed vulva
- Trichomonas vaginalis: itchy greenish-yellow frothy discharge with offensive smell
- Bacterial vaginosis: thin discharge with a fishy smell from the vagina
Candida vaginitis and bacterial vaginosis are NOT sexually transmitted diseases, even though sexual activity is a risk factor.
- Gonorrhoea causes cervicitis and rarely vaginitis. There is a purulent thin mucoid slightly yellow pus discharge with no smell and non-itchy
- Chlamydia causes cervicitis which may present with a non-itchy, thin, colourless discharge
Differential diagnosis
- Cancer of the cervix (blood-stained smelly discharge)
- Intra-vaginal use of detergents, chemicals, physical agents and herbs, chronic tampon use, allergic vaginitis
Investigations
- Speculum examination
- Pus swab: microscopy, Gram stain, C&S
- PH, KOH
- Blood: syphilis tests (RPR/VDRL)
- HIV Testing

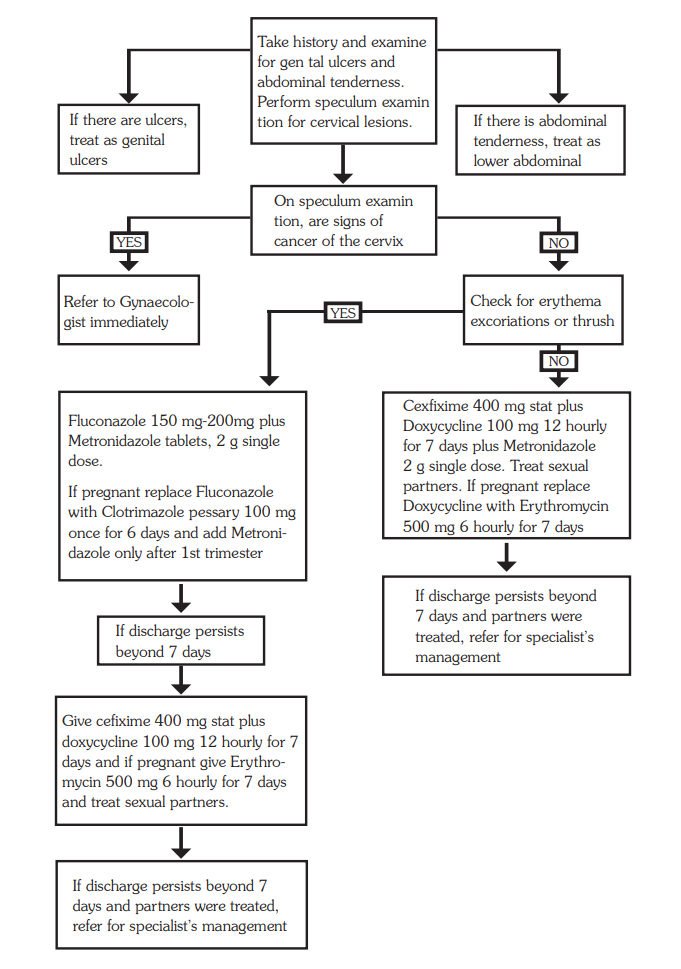
Management
Treatment
- Take history and examine for genital ulcers, abdominal tenderness
- Perform speculum examination for cervical lesions
- Assess risk for sexually transmitted disease
If there is lower abdominal tenderness and sexually active:
- Treat as in PID (see Pelvic Inflammatory Disease)
If no lower abdominal pain and discharge is thick and lumpy, vagina is itchy and erythema or excoriations are present: likely Candida
- Give clotrimazole pessaries 100 mg; insert high in vagina once daily before bedtime for 6 days or twice daily for 3 days
- Or fluconazole 200 mg tablets single dose, orally
- ± Metronidazole 2 g stat dose
If abundant/smelly discharge/vaginosis: possible trichomonas or vaginosis
- Metronidazole 2 g stat
If purulent discharge, or high risk of STD, or previous treatment non effective: treat for gonorrhea, and chlamydia, and trichomonas
- Give cefixime 400 mg stat or ceftriaxone 1g IV stat
- Plus doxycycline 100 mg 12 hourly for 7 days
- Plus metronidazole 2 g stat
However if client is pregnant
- Replace doxycycline with erythromycin 500 mg 6 hourly for 7 days or
- Azithromycin 1 g stat
- Treat the partner
If discharge or dysuria still persists and partners treated:
- Refer for further management
