Triage Overview
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Triage is the process of determining the priority of a patient to medical care based on the acuity (severity of condition) and capacity of the system to address the condition, so as to optimize outcome.
Importance of triage
Triage enables quick identification of patients who need immediate attention, and can thus improve patient outcomes by avoiding potential delays. It helps in organizing, monitoring, evaluating and determining the department resources that patients might need.
Triage system
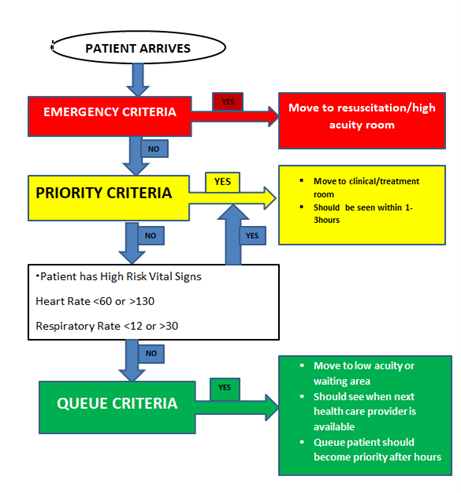
The triage system is based on recommendation of Emergency Medicine expert’s basic principles of triage, which uses specific criteria to categorize patients into three main levels of acuity:
Emergency: all patients with immediate life or limb threats who are deemed salvageable, but likely to further decompensate without immediate intervention will be triaged in this level. This category can also be labeled as RED
Priority: those seriously injured/ill patients with potential to decompensate if not treated within 1 hour are triage as priority cases. This category can also be labeled as YELLOW
Queue: this level includes all the walking wounded or those with less serious injury/sickness who are unlikely to decompensate. Patients in this category can safely wait for their turn. However, they should be monitored as their conditions may change and warrant immediate care. This category is also labeled as GREEN.
Figure 1. Summary of triage flow and timelines of care
|
EMERGENCY CRITERIA (Tick here if Yes) |
|||
|
Unresponsive |
Pregnant with Heavy bleeding |
||
|
Stridor |
Pregnant with Severe abdominal pain |
||
|
SpO2 <90% |
Pregnant with Seizures |
||
|
Respiratory distress or cyanosis |
Pregnant with Severe headache |
||
|
Weak pulse or Capillary refill>3 sec |
Pregnant with Visual changes |
||
|
Heart rate <50 or >150 |
Pregnant with SBP≥160 or DBP ≥110 |
||
|
Heavy bleeding |
Pregnant with Active labour |
||
|
Active convulsions |
Pregnant with Trauma |
||
|
Hypoglycemia |
Age < 2years with Temp <36oC or >39oC |
||
|
High-risk trauma* |
Child <14 with severe dehydration |
||
|
Poisoning or dangerous chemical exposure* |
Adult with signs of meningitis |
||
|
Threatened limb* |
Acute chest or abdominal pain (>50 years old) |
||
|
Snake Bite |
ECG with acute ischaemia |
||
|
Violent or aggressive |
Other (state): |
||
|
PRIORITY CRITERIA (TICK here is Yes) |
|||
|
Vomits everything or ongoing diarrhoea (adult) |
Severe pain (no Red criteria) |
||
|
Unable to feed or drink |
Visible acute lime deformity |
||
|
Severe Pallor |
Open fracture |
||
|
On-going bleeding (no emergency criteria) |
Suspected dislocation |
||
|
Recent fainting |
Other trauma/burns (no Red criteria) |
||
|
Altered mental status (no emergency criteria) |
Sexual assault |
||
|
Acute general weakness |
Acute tersticular/scrotal pain or priapism |
||
|
Acute focal neurology |
Unable to pass urine |
||
|
Acute visual disturbance |
Wheezing (no Red criteria) |
||
|
New rash worsening over hours or peeling (no emergency criteria) |
Exposure requiring time-sensitive prophylaxis (example: animal bite, needle-stick injury) |
||
|
Any infant 8 days to 2 months old |
Child below 14 years old with malnutrition |
||
|
Child below 14 years old with dehydration |
Child below 14 years old with ongoing diarrhoea |
||
|
Referral patient (no emergency criteria) |
Other, state: |
||
|
QUEUE CRITERIA (Tick here if Yes) |
|||
|
Patient with no Emergency or priority criteria indicated in above tables |
|||