- The persons with diabetes should receive a pre-Ramadan assessment ideally 6-8 weeks before the start of Ramadan.
- A detailed medical history on individuals should be obtained.
- Individual seeking to fast should be categorized as ‘high’, ‘moderate’ or ‘low’ risks based on the IDF-DAR Practical Guidelines 2021.
- Advice should be provided whether fasting is safe or not based on the risk category.
- Management plan should be individualized.
- To ensure safe fasting Ramadan-focused education is required consisting of:
- Diet plan
- Exercise pattern
- The frequency of SMBG
- When to break the fast
- Ramadan-oriented medication adjustment
6.6 Ramadan fasting
exp date isn't null, but text field is
6.6 Ramadan fasting13
- Should be individualized to an individual’s lifestyle requirements, age, comorbidities and other medical needs.
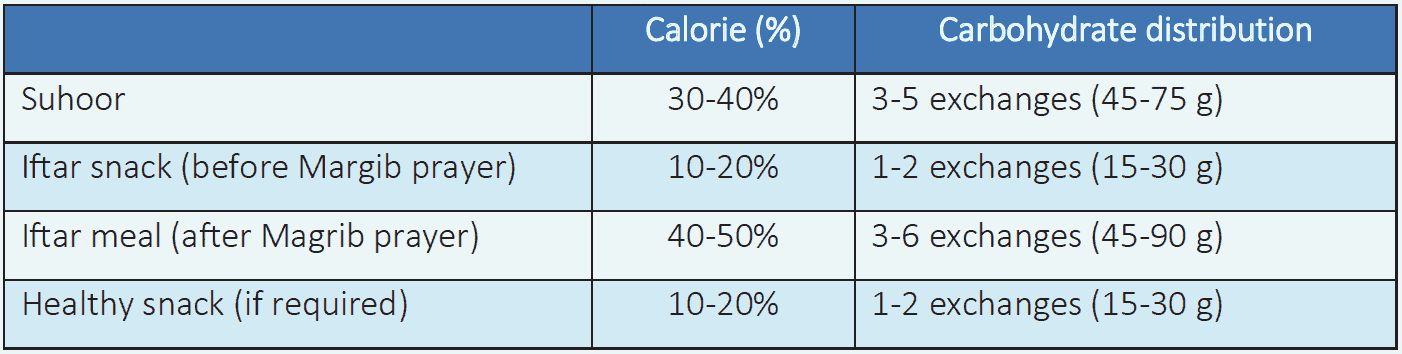
- Adequate daily calories should be divided between suhoor and iftar and 1-2 healthy snacks.
- Meals should be well balanced, with around 40–50% carbohydrates, preferably of a low GI source; the protein content (legumes, pulses, fish, poultry, or lean meat) should comprise 20–30%; and fat should comprise 30-35%; saturated fat should be limited to <10% of total calorie sugar-rich desserts should be avoided after iftar and between meals.
- Low GI carbohydrate should be selected, particularly those high in fibre (preferably whole grains). The consumption of carbohydrates from vegetables, whole fruits, yogurt, milk and dairy products are encouraged and from sugar and highly processed grains (wheat flour and starches like corn, white rice, and potatoes) should be avoided or minimized.
- Food rich in protein and good quality fat can better induce satiety than food rich in carbohydrates.1
Table 6.7 Calorie and carbohydrate distribution during Ramadan
- Physical activity should be reduced during day time
- Exercise can be performed after iftar or after tarawih
- Increased prayer during Ramadan should be taken into account while making plan for exercise
Table 6.8 Non-insulin antidiabetic agent dose adjustment
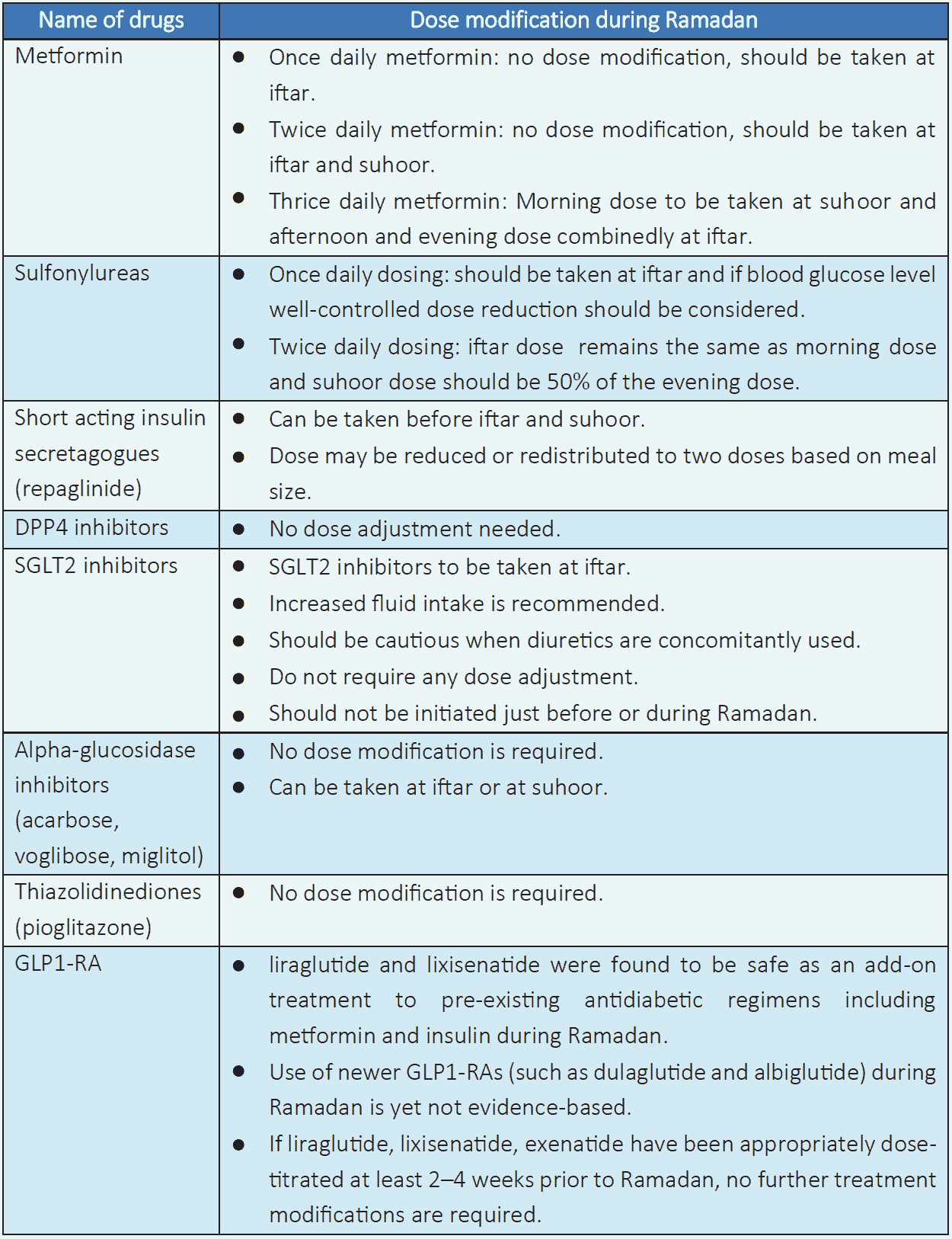
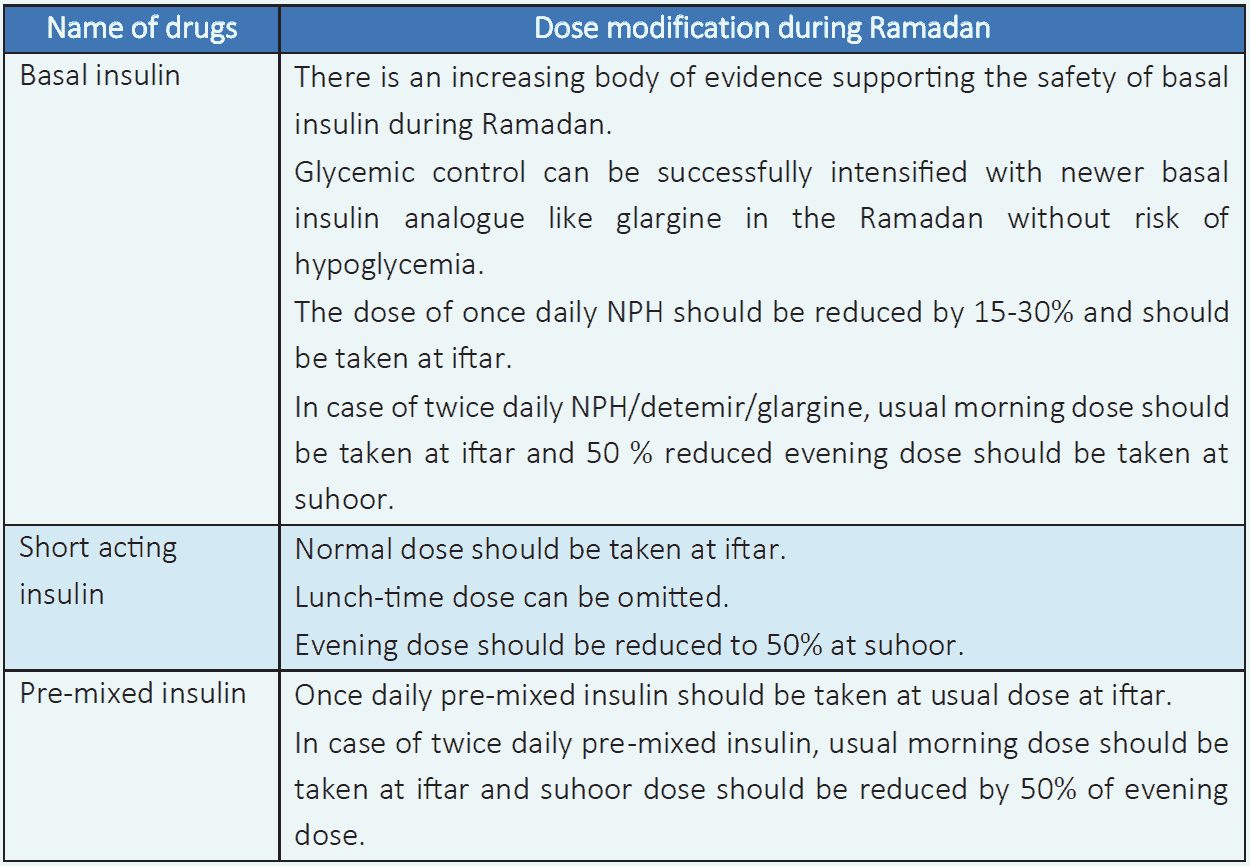
Table 6.9 Insulin dose modification during Ramadan
- Before iftar, 2 hours after iftar, mid-day and during any illness or symptoms of hypoglycemia.
- Frequency of SMBG should be daily for first 3 days, every 3rd day from next week onwards and every alternate day in the last week.
All individuals willing to fast should be advised to break the fast if:
- Blood glucose 3.9 mmol/L
- Blood glucose levels 16.6 mmol/L (for those with sudden rise of blood glucose level)
- Symptoms of hypoglycemia or acute illness occur
