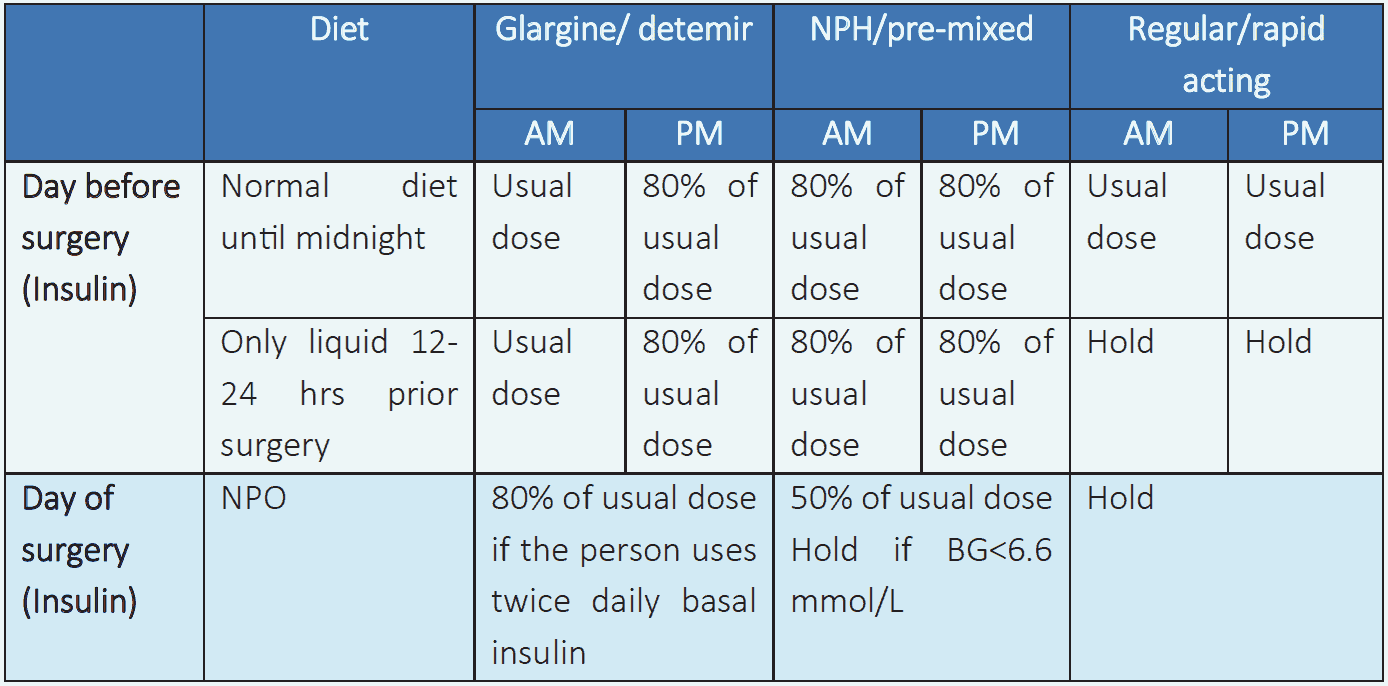
Insulin therapy should be initiated for treatment of persistent hyperglycemia at a threshold >10.0 mmol/L (checked on two occasions).
Once insulin therapy is started, a target glucose range of 7.8-10.0 mmol/L is recommended for the majority of critically ill and non-critically ill patients.1
Table 6.5 Insulin therapy in critical and noncritical setting1
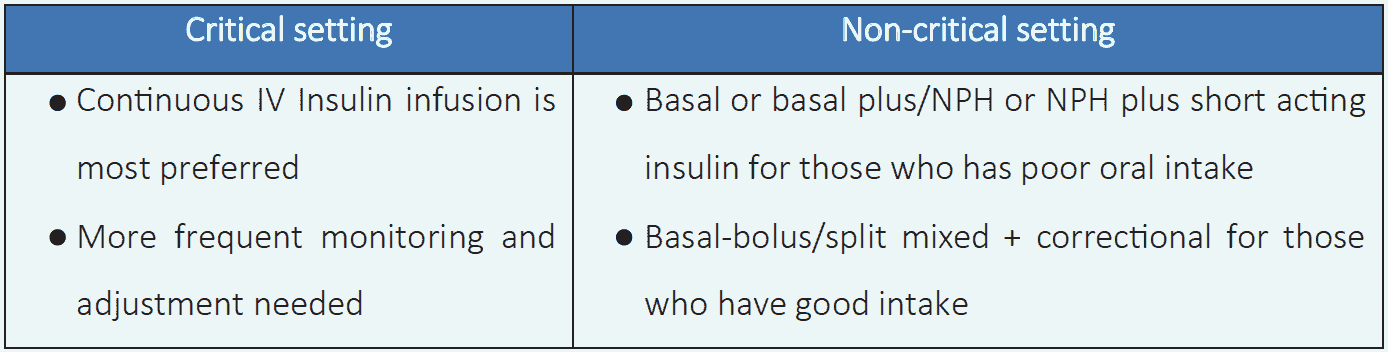
Insulin therapy1
- Insulin therapy is preferred for treatment of hyperglycemia in all hospitalized individuals.
- In noncritical setting, scheduled insulin regimen is recommended.
- Use of sliding scale insulin regimen is strongly discouraged.
- Pre-mixed insulin is not preferred in hospitalized patients.
- If oral intake is poor, a safer procedure is to administer prandial insulin immediately after the person eats.
Glucose monitoring in hospital1
- Those who are on oral feeding: bedside glucose monitoring before meals and 2 hours after meals.
- Those who are on NG tube/NPO: bedside glucose monitoring every 4-6 hours.
- In critical setting, who are on IV insulin: more frequent monitoring from every 30 minutes to 2 hours may be needed.