See Chapter 2.
6.2 Diabetes in children and adolescent
exp date isn't null, but text field is
Diabetes mellitus in childhood and adolescence is most often T1DM, but the incidence of T2DM is also increasing due to the rising rate of obesity among children, especially in Bangladesh.
In T1DM, insulin is the only choice. In T2DM, treatment modalities change according to age.
Table 6.3 Target level of glucose5
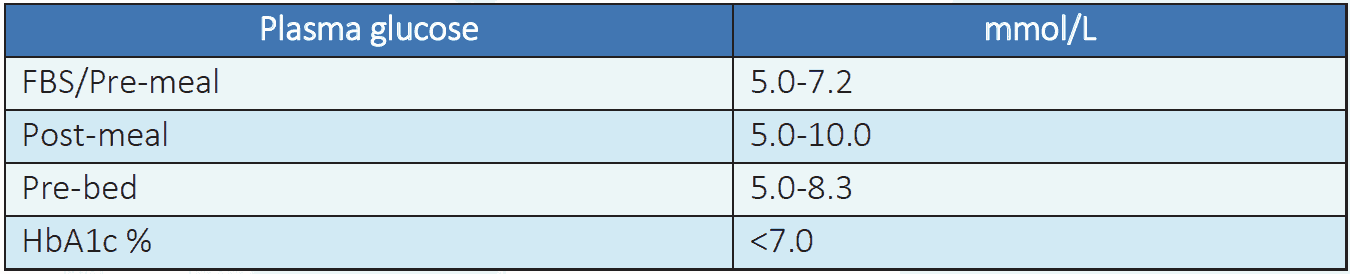
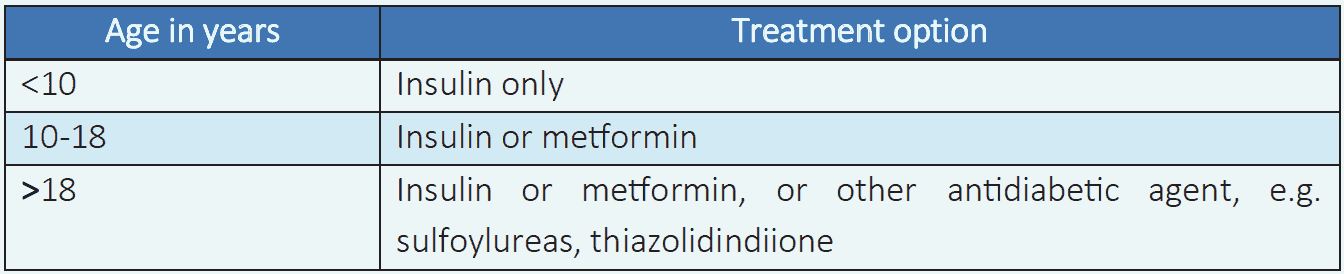
Table 6.4 Drug treatment of T2DM6
Diabetes education1
- Diabetes education is very essential part for effective management diabetes in this age group especially insulin injection technique, dietary practice, home monitoring of blood glucose etc. are needed. Providing emotional support is also very important.
- Infants and toddlers: They are totally dependent on parents and care providers for injections, food and monitoring. Need to be educated on prevention, recognition and management of acute complications, especially hypoglycemia, because it is very common complication in this age group.
- School going children: To be trained on Insulin injections and blood glucose monitoring, recognizing hypoglycemic symptoms, and understanding self-management, adapt to school programs, school meals, exercise and sports. Teacher/school authority should be involved in this learning process and parents are advised on the gradual development of the child's independence.
- Adolescents: Independent, responsible self-management appropriate to the level of maturity and understanding should be promoted.
Medical nutrition therapy (MNT)1
- All children with diabetes should be referred to a dietitian for counseling at diagnosis of diabetes and subsequently if they have problem with their diet adjustment.
- Age-specific calorie calculating charts are available for measuring diet allowance.
Sports and exercise1
- Children with T1DM with good blood glucose control can do all levels of exercise, including leisure activities, recreational sports and competitive professional performance. Exercise is more important for young T2DM, especially who are obese.
- Children between 3-5 years of age may take part in free play, walking, running etc.
- Children between 6-9 years of age may start learning to play team sports such as football, cricket etc.
- Children above 10 years of age and adolescents may be able to take part in all complex sports, like basketball, football, tennis, hockey etc.
6.2.3 Screening and treatment of complications and comorbidities6
Hypertension
- Blood pressure (BP) should be monitored at diagnosis and at every follow-up visit.
- Target BP (mmHg) < 90th percentile for age, sex, and height and if age >13 years old < 130/80.
- Lifestyle modification for elevated BP (90-95th percentile for age, sex, and height or if age > 13 years 120-129/<80).
- Lifestyle modification and ACEI or ARB for hypertension (>95th percentile for age, sex and height or if age >13 years old >130/80).
Dyslipidemia
- Lipid profile should be performed in children soon after diagnosis of DM (preferably after control of diabetes or age >2 year).
- If lipids are abnormal, annual monitoring is recommended.
- If LDL cholesterol values are within the accepted risk levels (<100 mg/dL), a lipid profile should be repeated every 3-5 years.
- Initial therapy includes blood glucose control and MNT.
- After the age of 10 years, statin is recommended in those who do not reach target (who have LDL cholesterol >160 mg/dL or >130 mg/dL with a cardiovascular risk factor) with lifestyle changes.
- The goal of therapy is LDL cholesterol value <100 mg/dL.
Nephropathy
- Albumin creatinine ratio (ACR) should be measured at puberty or age >10 years old whichever is earlier and diabetes duration of > 5 years.
- If normal screen annually, if abnormal it should be confirmed by repeating the test from 2 out of 3 sample in 6 months.
Retinopathy
Dilated fundoscopy should be performed to screen for retinopathy at puberty or at age >11 years old whichever is earlier and diabetes duration of 3-5 years. If normal, every 2 years.
Neuropathy
Foot examination with foot pulse, pinprick, vibration test, ankle jerk and 10-gm monofilament sensation test (if possible) should be performed at puberty or at 11 years of age whichever is earlier and diabetes duration of 5 years. If normal, annually.
Other autoimmune disease
For those with type 1 diabetes advise for thyroid function test and IgA of tTG for celiac disease if possible soon after diagnosis.
