Medical nutrition therapy
- MNT should be started soon after diagnosis of GDM preferably by dietitian and reviewed in each trimester.
- The aim is to achieve normoglycemia, adequate maternal weight gain, adequate fetal growth, prevention of ketosis.
Table 6.1 Recommended weight gain during pregnancy based on pre-pregnancy BMI3
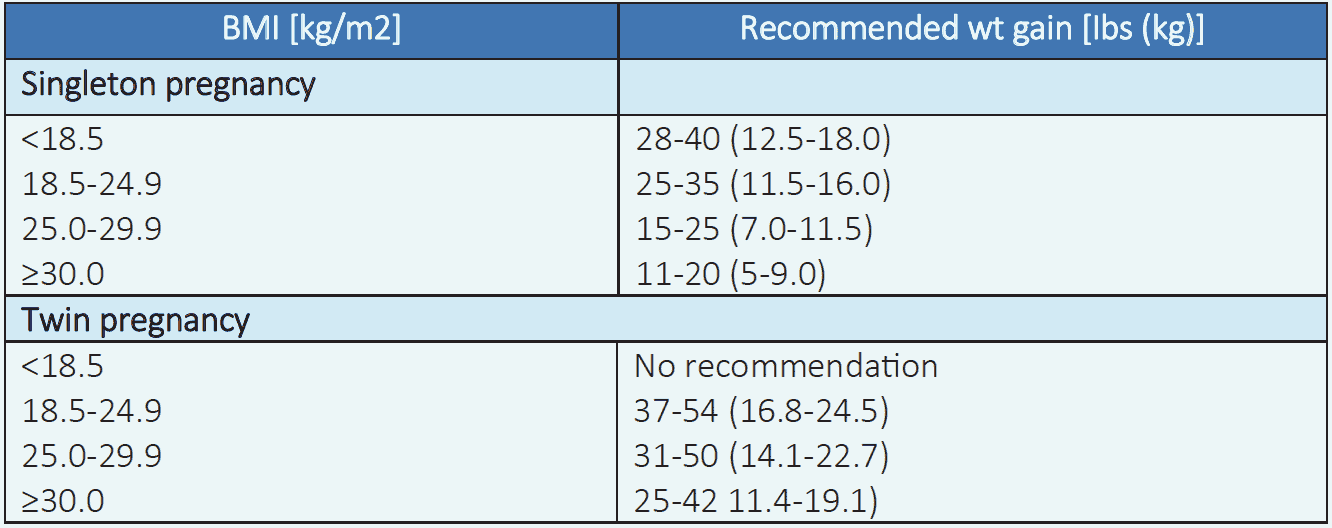
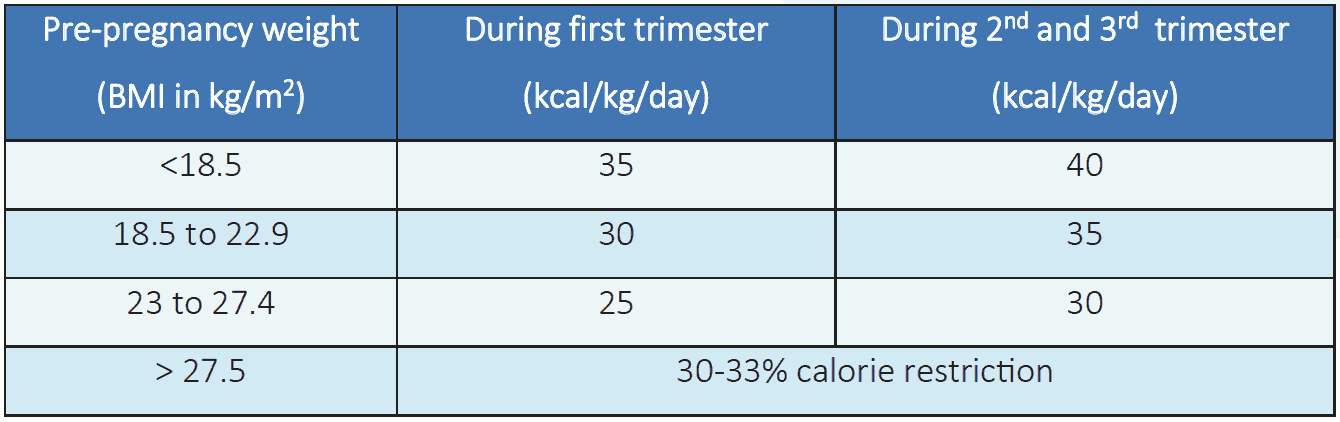
Table 6.2 Daily calorie allocation according to pre-pregnancy weight3
Meal pattern
3 main meals and 3 snacks should be taken including 1 snack at bed time.
Recommended overall total caloric distribution3
- Carbohydrate: 33-40% with low glycemic index
- Protein: ~ 20%
- Fat: <40%, saturated fat <7% and transfat <1%
- Simple sugars should be avoided. Food containing complex carbohydrate is recommended
- High dietary fiber and whole grain containing foods should be encouraged
- Non-calorie sweeteners (aspartame) may be used safely
- Lean protein, oily fish and vegetable consumption should be increased
- Recommended daily requirement of iron- 30 mg, calcium- 1000 mg and folate- 0.6 mg
Physical activity1
- Moderate exercise, aerobic, resistance or both are effective. Duration of exercise can be 20-50 minutes/day, 2-7 days/week of moderate intensity.
- While doing exercise excessive abdominal muscular contracture should be avoided.
Pharmacological management
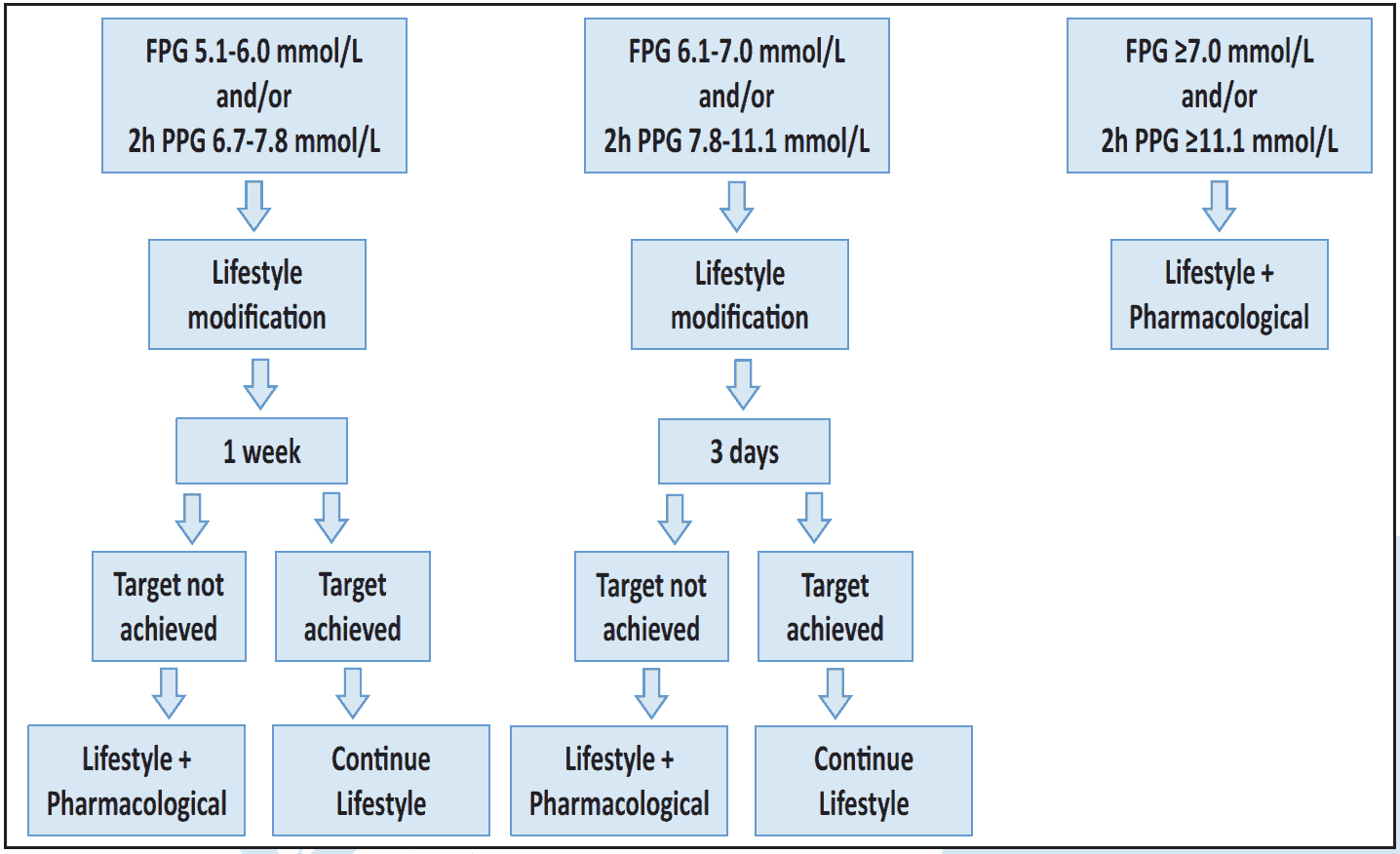 Figure 6.1 Diabetes management during first and third trimester3
Figure 6.1 Diabetes management during first and third trimester3
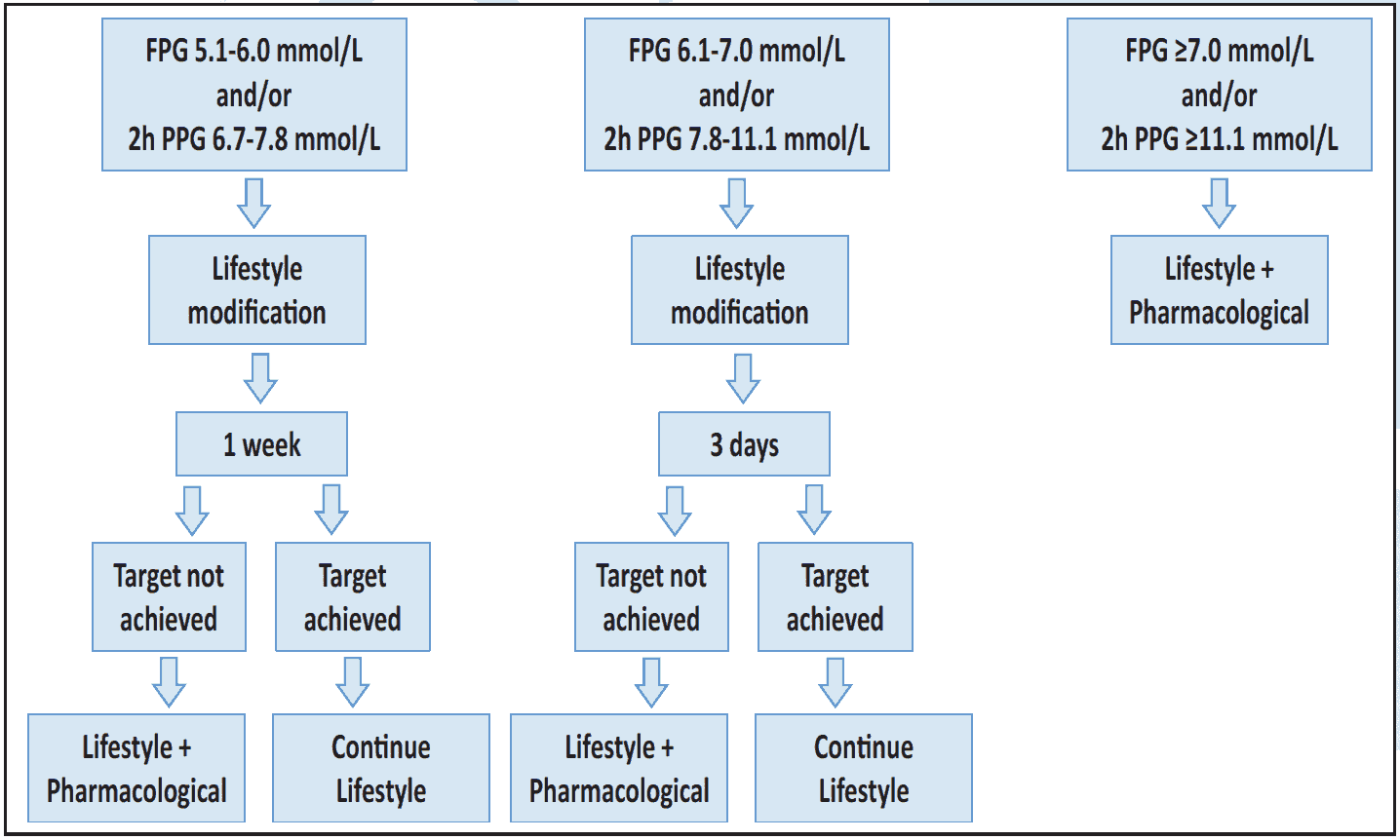 Figure 6.2 Diabetes management during second trimester3
Figure 6.2 Diabetes management during second trimester3
Recommended insulins
- Recombinant human short and intermediate (NPH) acting insulin
- Rapid acting analogue aspart and lispro
- Long-acting analogue detemir
- Required initial daily dose is 0.2 to 0.5 unit/kg body weight. Obese women may need higher dose Treatment should be graded to reach the targets
Approach to start insulin
Step 1: Raised post meal blood glucose should be controlled by bolus insulin – either by regular/short acting human insulin or by short/ultra-short acting analogue with meal(s) and titrated frequently to reach the post-meal targets.
Step 2: High FPG should be controlled with intermediate acting human insulin (NPH) or basal analogue insulin in a lower dose then titrated to reach the target.3
- Only bolus insulin may be needed in some cases of GDM when FPG is well controlled
- Pre-mixed insulin is usually not preferred
- Non-insulin antihyperglycemic agents are not recommended
Target 1
- Fasting blood glucose <5.3 mmol/L (95 mg/dL)
- 2-hour post-prandial glucose <6.7 mmol/L (120 mg/dL)
Glucose monitoring
- Every woman should be offered education and encouraged for self-monitoring of pre- and post-meal glucose at home, twice or thrice a week.
- HbA1c should be used as secondary measure of glycemic control, after blood glucose monitoring.
Management during labor4
- Hospital delivery is mandatory.
- Indications for C/S are the same for those with other women.
- Maternal glucose should be maintained between 4.0 to 7.0 mmol/L during labor.
- Most women who require <1.0 unit/kg/day insulin can simply be monitored without intravenous Insulin.
- If needed infusion of 5% Dextrose with short acting Insulin can be maintained but Glucose-Insulin infusion should be stopped immediately after delivery.
- Blood glucose of newborn should be seen by heel prick within half an hour.



 Figure 6.1 Diabetes management during first and third trimester3
Figure 6.1 Diabetes management during first and third trimester3 Figure 6.2 Diabetes management during second trimester3
Figure 6.2 Diabetes management during second trimester3