5.5 Cardiovascular diseases
exp date isn't null, but text field is
More than 70% people with DM die due to cardiovascular causes.
5.5.1 Screening
Screening for coronary artery disease should be done in symptomatic persons and people with risk for cardiovascular disease.
5.5.2 Treatment
- ACE inhibitor or angiotensin receptor blocker
- SGLT2 inhibitors and GLP1-RA
- Statins
- Aspirin and/or clopidogrel
- Selective beta-blockers should be continued for at least 2 years after the event
5.5.3 Hypertension
Hypertension is a common comorbidity of DM.
- Blood pressure should be measured in every follow-up.
- Target is <130/80 mmHg for non-pregnant adult.
- If blood pressure is >130/80 mmHg but <140/90mmHg, then lifestyle modification.
- If blood pressure is >140/90 mmHg, recheck after 1 week. If still high then lifestyle modification and monotherapy.
- If blood pressure is >160/100 mmHg, start dual antihypertensive.
- The choice can be ACE inhibitor or ARB, Calcium channel blocker and diuretics.
- Selective beta blocker or alpha blocker can be used in special situation.
5.5.4 Dyslipidemia
Diabetic dyslipidemia is very common. Screening and Monitoring of lipid profile should be done at the time of diabetes diagnosis, at an initial medical evaluation, yearly and more frequently if indicated.
Table 5.4 Targets of blood lipids in person with DM6
Treatment
Lifestyle modification:
- Maintain ideal body weight
- Avoid saturated and trans fats
- Increase dietary omega-3 fatty acids, fibers, and green leafy vegetables and fresh fruits
- Increased physical activity
Table 5.5 Pharmacological therapy based on age, ASCVD or ASCVD risk factors6,7
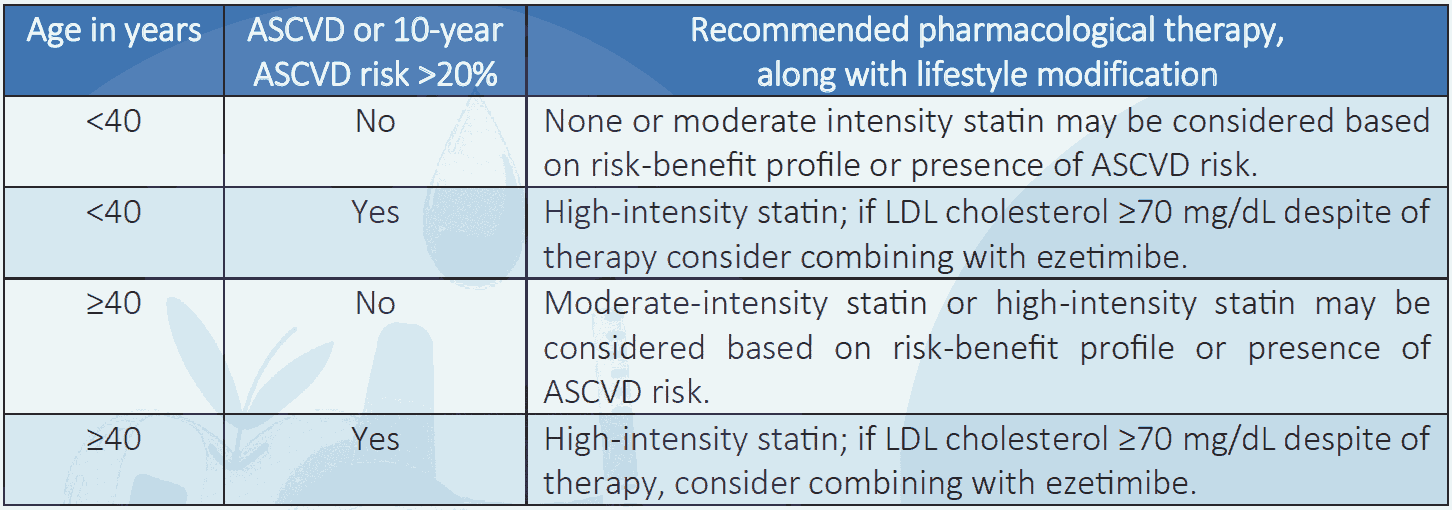
NB: Intensity of statin therapy may need to be adjusted according to individual response to medication (e.g. side effects, tolerability, LDL cholesterol levels, etc.).
5.5.5 Antiplatelet agents6
- Aspirin therapy (75–150 mg/day) as a secondary prevention strategy in those with diabetes and a history of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease.
- Persons with atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease and documented aspirin allergy, clopidogrel (75 mg/day) should be used.
- Dual antiplatelet therapy is reasonable for a year after an acute coronary syndrome.
- For primary prevention of ASCVD, aspirin is recommended for those with diabetes and age >50 years, having at least one major risk factor for ASCVD.
