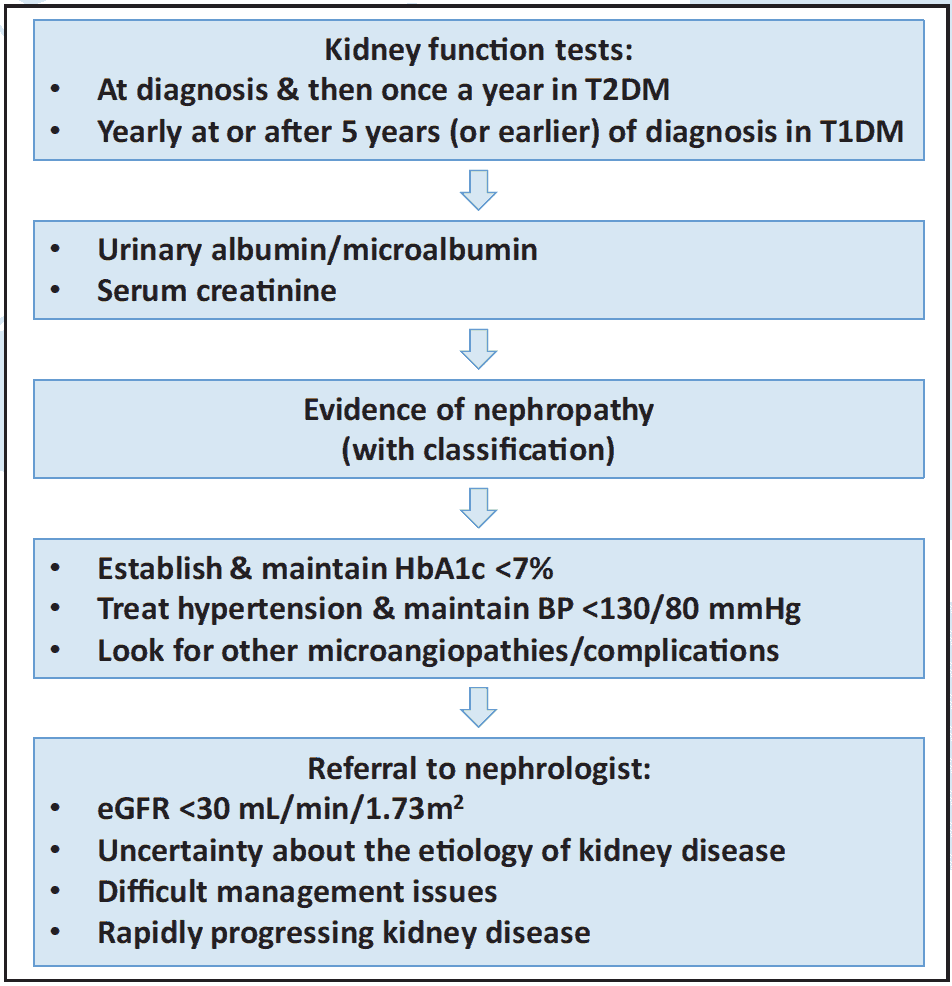
- Albumin-to-creatinine ratio (ACR) is the preferred method to detect elevated protein in urine. The recommended method to evaluate albuminuria is to measure urinary ACR in a spot urine sample (preferably morning fasting sample before exercise).
- ACR is calculated by dividing albumin concentration in milligrams by creatinine concentration in grams.
- Normal: ACR <30 mg/g, normal to mildly increased albuminuria.
- Microalbuminuria: ACR 30-<300 mg/g, moderately increased albuminuria.
- Macroalbuminuria: ACR >300 mg/g, severely increased albuminuria.2
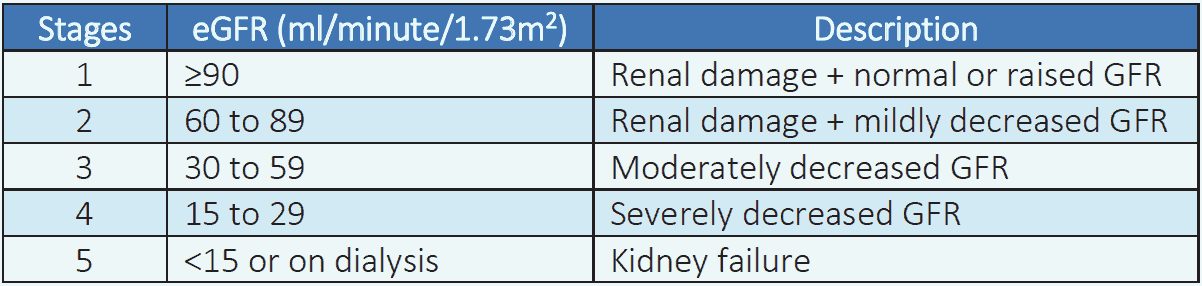
Table 5.1 Stages of CKD by eGFR3
Markers of renal damage (one or more)4
- Albuminuria (AER ≥30 mg/24 hours; ACR ≥30 mg/g [≥3 mg/mmol])
- Urine sediment abnormalities
- Electrolyte and other abnormalities due to tubular disorders
- Abnormalities detected by histology
- Structural abnormalities detected by imaging
- History of kidney transplantation